Rare Disease Directory
1. What is a rare disease?
Rare disease, also known as "orphan disease", refers to a type of disease with a very low incidence and a small number of patients within a certain period of time.
Among them, 80% are hereditary diseases, 90% are serious diseases, and 50% are found in children. They are often characterized by severe disability and lethality, complex pathogenesis, and difficult diagnosis and treatment.
The World Health Organization defines rare diseases as the diseases that affect 0.65% to 1% of the total population.
According to the definition in the Research Report on the Definition of Rare Diseases in China 2021, in our country, rare diseases are those with a neonatal incidence rate of less than 1/10,000, a prevalence rate of less than 1/10,000, and a prevalence of less than 140,000.
2. How many rare diseases are there?
There are more than 7,000 rare diseases that have been identified, but this number is not fixed. In recent years, with the rapid development of genetic testing technology, about 200 new diseases are discovered every year.
According to the Catalogue of the First Batch of Rare Disease jointly formulated by the National Health Commission and other four departments, there are 121 rare diseases in China.
https://m.wang1314.com/doc/webapp/topic/21084617.html
3. What are the common rare diseases?
1. Baby Butterfly - Epidermolysis Bullosa (EB)
Epidermolysis bullosa is a rare inherited skin disorder.
Since the patient lacks the specific gene for the production of epithelial cell adhesion proteins, the epidermis does not adhere to the dermis effectively, so that slight impact or friction (clothes, diapers, shoes, gloves, etc.) can cause blisters to form on the skin/mucosal surface, just as fragile as the wings of a butterfly.
When the blisters burst, the skin is exposed and difficult to heal, and there is a greater risk of infection. Extensive skin damage can lead to fluid imbalances and protein depletion. Mucosal involvement may cause malnutrition, stunting, respiratory disturbances, and urogenital disorders.
2. Albinism

Albinism is attributed to the skin disease system, it generally manifests as autosomal recessive inheritance. The disease is a hereditary diseases caused by the lack of melanin in the eyes or eyes, skin, and hair caused by the mutations of a group of gene related to melanin synthesis.
The patients are characterized by white or pink skin, white or yellowish hair, and symptoms such as low vision, photophobia, and nystagmus.
3. ALS - Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) is a chronic progressive degenerative disease widely known because of the "Ice Bucket Challenge" project, which affects both the upper motor neuron (UMN) and the lower motor neuron (LMN) and the trunk, extremities, and craniofacial muscles under its innervation.
The main symptoms of patients are muscle weakness, muscle atrophy, fasciculation, bulbar palsy and pyramidal tract signs.

4. Porcelain Doll - Osteogenesis imperfecta (OI)
Osteogenesis imperfecta, also known as brittle bone disease, has an incidence rate of about 1 in 10,000 to 1 in 15,000. There are about 100,000 patients in China. It is a dominantly inherited pain disease.
The disease is generally manifested as bone fragility and bone deformity. In severe cases, a gentle hug can also lead to fractures. If not treated in time, it will lead to lifelong disability.
The main characteristics of patients are: frequent fractures, short stature, progressive hearing loss, blue eyes and sclera, etc. Because patients are prone to fractures, they are commonly known as "porcelain dolls".
5. Glass Doll - Hemophilia
Hemophilia is a hereditary hemorrhagic diseases caused by the lack of a group of certain coagulation factors in the blood that lead to severe coagulation disorders in patients. It could be found in both males and females, mostly in the former.
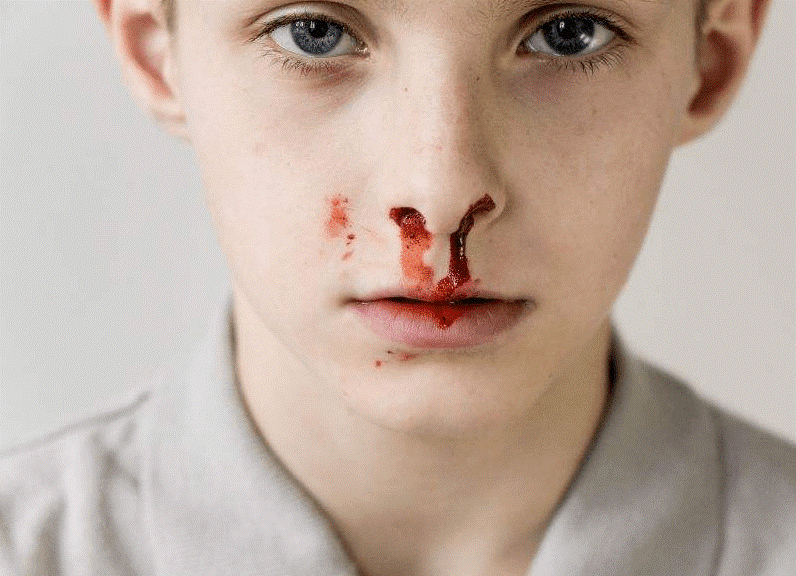

Hemophilia is the most common congenital bleeding disorder, and bleeding is the main clinical manifestation. Because people with hemophilia are prone to bruising or bleeding after being bumped or traumatized, they are called "glass dolls" that cannot be touched or dropped.
6. Hard Skin Disease - Systemicscleroderma (SSc)
The most obvious characteristic of SSc is the hardening of the skin. It is a connective tissue disease characterized by hyperplasia and sclerosis of collagen fibers in the skin and various systems. It can affect multiple internal organs such as the heart, lungs, kidneys, and digestive tract, and is often accompanied by immune abnormalities and microvascular lesions.
At present, the etiology of SSc is still unclear, and the pathogenesis is complex. According to the degree of skin thickening and the extent of lesion invasion, it is divided into focal SSc and systemic SSc.
7. Klinefelter Syndrome

Klinefelter syndrome is a genetic disorder caused by abnormal sex chromosomes. The individual has at least 2 XX sex chromosomes and at least 1 Y sex chromosome, typically XXY, observed usually in male.
Klinefelter syndrome itself is not fatal, and the physical and mental distress of the patient is caused by complications and comorbidities. Its common complications and complications include: mammary gland hyperplasia, osteoporosis, type 2 diabetes, systemic lupus erythematosus, autism, breast cancer and so on.
8. Happy Puppet/Angel Baby - Angelman Syndrome
Angelman syndrome is a disease caused by a genetic defect. Patients suffering from this disease often have smiles on their faces, lack of language capabilities, move excessively, and have low intelligence.
Apart from the smiles, robot-like motions and low intelligence, they also has symptoms such as epilepsy. Symptoms also include frequent laughter, raised hands, waving, unsteady feet, spasms, lack of language capabilities and mental retardation, hence the disease is also called "Happy Puppet Syndrome".

9. Huntington's Disease (HD)
Huntington's disease is a rare autosomal dominant genetic disease. The main cause is the mutation of the huntingtin gene on the fourth chromosome, which produces a mutated huntingtin protein, which eventually leads to neurological dysfunction and degeneration.
Such disease typically presents in middle age with motor, cognitive, and psychiatric symptoms. The onset is insidious and the progression is slow, and the main features of the disease are chorea-like movements with progressive cognitive and mental dysfunction and eventually dementia. Patients generally survive 15-20 years after the onset.
10. Spinal Muscular Atrophy (SMA)
Spinal muscular atrophy is a type of disease in which the degeneration of motor neurons in the ventricornu that leads to muscle weakness and muscle atrophy. It is an autosomal recessive genetic disease, and the clinical manifestations are quite different. Based on the age of onset and clinical course of the patient, SMA is divided into 4 types from severe to mild.
The common feature is the degeneration of the ventricornu, and the clinical manifestations are progressive, symmetrical, generalized flaccid paralysis and muscle atrophy mainly in the proximal part of the limbs, whiel the mental development and sensation are normal.
4. How difficult is the diagnosis and treatment of rare diseases?
1. The first difficulty is diagnosis.
"Fewer doctors who cure rare diseases than patients" is the consensus of experts in the field of rare disease treatment.
The wide variety and insufficient cases of rare diseases make it difficult for doctors to diagnose, resulting in a high incidence of misdiagnosis and missed diagnosis. Through the long treatment period, the best timing could be left slip, only the aggravating condition remains.
2. The second difficulty is drugs.
Because of the low incidence of rare diseases, their attention and corresponding research resources are very limited. Compared with rare diseases with few patients, those diseases with a large base of patients can obtain huge returns, so pharmaceutical companies have little interest in investing in drug research and development for rare diseases.